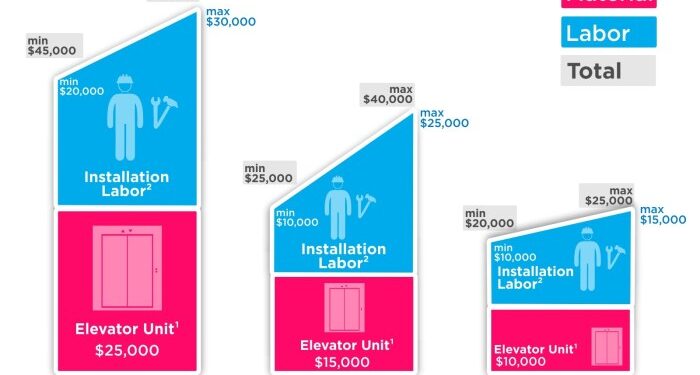
When it comes to installation projects, one crucial aspect that can make or break the budget is the installation cost. Understanding the various factors that impact these costs is essential for effective planning and budgeting. From materials to labor to unforeseen expenses, each element plays a role in determining the final price tag of an installation.
Let’s delve deeper into the world of installation costs and unravel the mysteries behind them.
Factors affecting installation cost
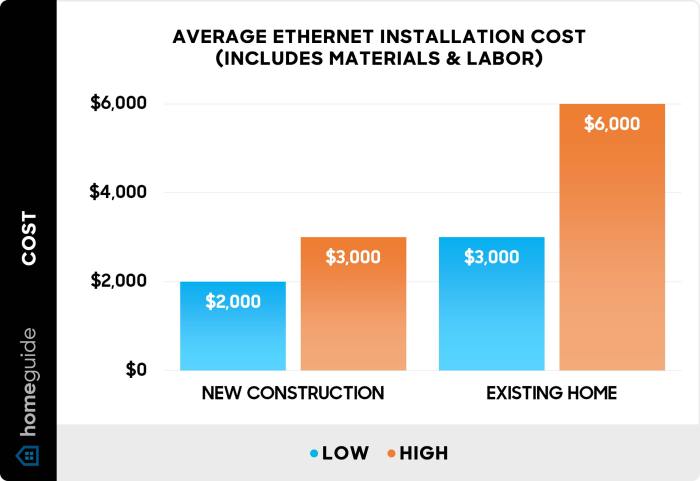
Factors affecting the installation cost can vary significantly depending on various elements that influence the overall expenses. Understanding these key factors is crucial for estimating and managing installation costs effectively.
1. Type of equipment or system
The type of equipment or system being installed plays a significant role in determining the installation cost. Complex systems or specialized equipment often require more time and expertise to install, leading to higher labor costs. For example, installing a simple residential HVAC system may be less expensive compared to a commercial-grade system with advanced features.
2. Labor costs
Labor costs are a major factor influencing installation expenses. The skill level of the technicians, the complexity of the installation process, and the duration required for completion all contribute to the overall labor costs. Highly skilled technicians may charge more for their services, especially for intricate installations that demand expertise.
3. Location and accessibility
The location of the installation site and its accessibility can impact the overall installation cost. Difficult-to-reach locations, such as high-rise buildings or remote areas, may require additional equipment or manpower, leading to higher expenses. Accessibility issues can also prolong the installation process, further increasing costs.
4. Material costs
The cost of materials needed for the installation also plays a crucial role in determining the total expenses. High-quality materials or specialized components may come at a premium, adding to the overall installation cost. Additionally, the quantity of materials required for the installation can influence the final bill significantly.
5. Permits and regulations
Obtaining necessary permits and complying with building regulations can add to the installation cost. Fees associated with permits, inspections, and ensuring compliance with safety standards contribute to the overall expenses. Failure to adhere to regulations can result in fines or delays, further impacting the installation cost.
6. Project scope and timeline
The scope of the installation project and the timeline for completion can affect the overall cost. Larger projects or those with strict deadlines may require additional resources and manpower, leading to higher expenses. Delays in the project timeline can also result in increased costs due to extended labor hours or rescheduled appointments.
7. Warranty and maintenance
Including warranties or maintenance agreements in the installation package can impact the overall cost. Opting for extended warranties or maintenance plans may result in higher upfront costs but can provide long-term savings by covering future repairs or servicing. Considering these factors can help in making informed decisions about installation costs.
Types of installation costs
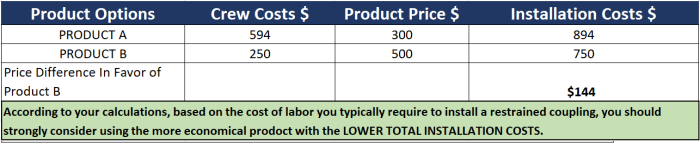
When it comes to installation projects, there are various types of costs involved that contribute to the total installation cost. These costs can be categorized into direct and indirect costs, each playing a crucial role in determining the overall expenses of the project.
Direct Installation Costs
Direct installation costs are expenses that can be directly attributed to the installation process itself. These costs typically include labor, materials, equipment, and any other resources specifically required for the installation. For example, in a solar panel installation project, the cost of solar panels, mounting hardware, and the wages of the installation crew would all fall under direct installation costs.
These costs are essential and directly impact the quality and efficiency of the installation.
Indirect Installation Costs
On the other hand, indirect installation costs are expenses that are not directly tied to the installation process but are necessary for the project’s completion. These costs may include permits, licensing fees, administrative expenses, insurance, and overhead costs. While indirect costs may not be as visible as direct costs, they are crucial for the smooth running of the installation project.
For instance, obtaining permits and paying licensing fees are essential steps that need to be accounted for in the overall installation cost.
Components of Total Installation Cost
The total installation cost is a combination of both direct and indirect costs. It is important to consider all the components that make up the total cost to ensure accurate budgeting and planning. By understanding the breakdown of costs, project managers can make informed decisions and allocate resources efficiently to complete the installation successfully.
Real-life Examples
In a home renovation project, direct installation costs may include the cost of materials such as flooring, paint, and fixtures, as well as the labor costs for carpenters, plumbers, and electricians. On the other hand, indirect installation costs may involve obtaining building permits, hiring a project manager, and paying for insurance coverage.
These examples illustrate how different types of costs can vary in installation projects and highlight the importance of considering all cost components for effective project management.
Cost estimation methods
Accurately estimating installation costs is crucial for project planning and budgeting. Various methods are utilized to estimate these costs, each with its own advantages and limitations.
Historical Data Analysis
One common method is using historical data analysis, where past projects with similar scope and requirements are analyzed to determine the cost of installation. This method relies on the assumption that past costs can provide a reliable estimate for future projects.
Bottom-Up Estimation
Another method is bottom-up estimation, which involves breaking down the installation project into smaller components and estimating the cost of each component individually. These individual estimates are then aggregated to arrive at the total installation cost.
Analogous Estimation
Analogous estimation is based on comparing the current installation project with similar projects completed in the past. By adjusting the cost of the previous project based on the differences in scope, scale, and other factors, an estimate for the current project can be derived.
Parametric Estimation
Parametric estimation uses mathematical models and algorithms to estimate installation costs based on specific project parameters, such as square footage, number of units, or other measurable variables. This method is often used for projects with repetitive elements that can be quantified.
Importance of Accurate Cost Estimation
Accurate cost estimation is vital for project planning as it helps in setting realistic budgets, allocating resources efficiently, and ensuring the financial viability of the project. Without accurate estimates, projects may face cost overruns, delays, and potential failure.
Comparison of Estimation Techniques
| Estimation Technique | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Data Analysis | Relies on actual project data | May not account for changes in market conditions |
| Bottom-Up Estimation | Provides detailed cost breakdown | Time-consuming and resource-intensive |
| Analogous Estimation | Quick and easy to apply | Dependent on similarity to past projects |
| Parametric Estimation | Useful for repetitive projects | Requires accurate input parameters |
Cost-saving strategies in installations
When it comes to reducing installation costs, there are several practical strategies that can be implemented to lower expenses without compromising quality. Efficient planning plays a crucial role in minimizing costs and ensuring a successful installation process. By adopting innovative approaches and investing in cost-saving strategies, businesses can reap long-term benefits and enhance their overall profitability.
Optimizing Resource Allocation
One of the key strategies to save costs during installations is optimizing resource allocation. This involves carefully planning and scheduling the use of resources such as labor, materials, and equipment to avoid unnecessary wastage and delays. By streamlining the allocation of resources, businesses can reduce installation time and minimize costs significantly.
- Utilize a just-in-time approach to minimize excess inventory and storage costs.
- Implement efficient workflow processes to enhance productivity and reduce labor expenses.
- Regularly monitor resource usage and adjust plans accordingly to avoid overruns.
Exploring Alternative Technologies
Another cost-saving strategy is to explore alternative technologies that can help lower installation costs. This may involve using innovative tools, equipment, or techniques that are more efficient and cost-effective than traditional methods. By embracing technological advancements, businesses can reduce labor hours, improve productivity, and ultimately save on installation expenses.
- Invest in automation tools or robotics to streamline installation processes and reduce labor costs.
- Consider modular or prefabricated components to minimize on-site construction time and labor expenses.
- Explore energy-efficient solutions that can lead to long-term cost savings through reduced utility bills.
Prioritizing Preventive Maintenance
Prioritizing preventive maintenance is another effective strategy to lower installation costs in the long run. By proactively maintaining equipment, systems, and infrastructure, businesses can prevent costly breakdowns, repairs, and replacements down the line. Regular maintenance not only extends the lifespan of installations but also helps avoid unexpected expenses that can arise from neglect.
- Establish a comprehensive maintenance schedule to ensure regular inspections and upkeep of installations.
- Train staff on proper maintenance procedures to minimize the risk of costly repairs or replacements.
- Utilize predictive maintenance technologies to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
Closing Notes
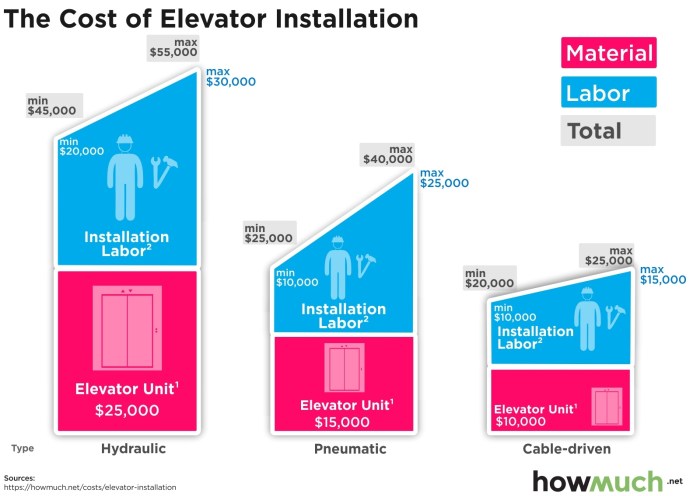
In conclusion, installation costs are a complex interplay of multiple factors that require careful consideration and planning. By understanding the nuances of these costs and implementing effective strategies, one can successfully manage and control installation expenses. Remember, a well-planned project leads to not only cost savings but also ensures a smooth and efficient installation process.
FAQ Explained
What are the key factors that influence installation cost?
The key factors include materials used, labor costs, project complexity, location, and any unforeseen expenses.
What is the difference between direct and indirect installation costs?
Direct costs are directly attributable to the installation project, while indirect costs are associated but not directly tied to the project itself.
How important is accurate cost estimation in project planning?
Accurate cost estimation is crucial as it forms the basis for budgeting, resource allocation, and overall project success.
What are some cost-saving strategies that can be implemented during installations?
Strategies such as efficient planning, bulk purchasing, and utilizing innovative approaches can help reduce installation costs without compromising quality.
What are the benefits of investing in cost-saving strategies for installations in the long run?
Investing in cost-saving strategies not only lowers immediate expenses but also leads to long-term savings, improved efficiency, and better project outcomes.